Fed model of stock market valuation
The beginning of the 21st century was witness to the advancement of the Fed Model as a stock valuation methodology by Wall Street gurus and the financial press.
The Fed Model compares stock yield versus bond yield. Proponents almost always point to the following three attributes to explain its popularity:. This article will take a look at the basic ideas behind the Fed Model - how it works and how it was developed.
We will also discuss challenges to its success and theoretical soundness. What Is the Fed Model? Some advocates of the Fed Model think the yield relationship varies over time, so an average of each period's yield comparison is used.
The more popular method appears to be one where the relationship is fixed at the particular value of zero. This technique is referred to as the strict form of the Fed Model because it says the relationship is strict equality. The premise behind the model is that bonds and stocks are competing investment products.
An investor is constantly making choices between investment products as the relative prices between these products change in the market place. Origins The name "Fed Model" was manufactured by Wall Street professionals in the late s and it's important to note that this system is not officially endorsed by the Federal Reserve Board.
He named the relationship the "Fed's Stock Valuation Model", and the name stuck. The original use of this type of analysis is not known, but a bond yield versus equity yield comparison has been used in practice long before the Fed graphed it out and Yardini began marketing the idea.
Whatever Happened to the Fed Model? -- The Motley Fool
One would suspect that due to its simplicity this type of analysis was probably in use some time before that as well. Stock Returns, Earnings, and Mean Reversion ," Robert Weigand and Robert Irons comment that empirical evidence suggests that investors began using the Fed model in the s soon after Myron Gordon described the Dividend Discount Model in the seminal paper "Dividends, Earnings and Stock Prices" in This analysis is typically done by looking at the difference between the two expected returns.
In general, the bigger the spread, the cheaper stocks are supposed to be relative to bonds and vice versa. This valuation suggests a falling bond yield dictates a falling earnings yield which will ultimately result in higher stock prices.
That is P S should rise for any given E 1 when bond yields are below the stock yield. Sometimes financial market pundits carelessly or possibly ignorantly say, "Stocks are undervalued according to the Fed Model or interest rates. It may be that stocks are expensive and priced to deliver returns below their average long-run returns, but bonds are even more expensive and priced to deliver returns far below their average long-run returns.
It could be possible that stocks could continuously be undervalued according to the Fed Model while stock prices fall from their current levels. Observational Challenges Opposition to the Fed Model has been based on both empirical, observational evidence and theoretical shortcomings. To begin, although stock and long-term bond chase online stock trading appear to be correlated from the s forward, they appear to be far from correlated prior to the s.
Also, there may be statistical issues in the way the fed model easiest games to make money on neopets been calculated. Originally, statistical analysis was conducted using ordinary least-squares regressionbut it may appear that both bond and stock yields are co-integrated, which would require a different method of statistical analysis. Professor Javier Estrada wrote a paper in called "The Fed Model: The Bad, The Worse, And The Ugly" where he looked into the empirical evidence using the more appropriate co-integration methodology.
His conclusions suggest that the Fed model may not be as good of a tool as originally thought. Theoretical Challenges Opponents of the Fed Model also pose interesting and valid challenges to its theoretical soundness.
Concerns arise over comparing stock yields and bond yields because Y B is the internal rate of return IRR of a bond and accurately represents the expected return on bonds. This difference causes a breakdown in the expected return comparison. Opponents argue that inflation does not affect stocks like it does bonds.
It is typically assumed that inflation will be passed through to stock holders via earnings, but coupons to bond holders are fixed. So, when the bond yield rises due to inflation, P S is not affected because earnings rise by an amount that offsets this increase in the discount rate. Thus in periods of high inflation the Fed Model will incorrectly argue for a high stock yield and depress stock prices, and in low inflation it will incorrectly argue for low stock yields and increase stock prices.
The above circumstance is called fed model of stock market valuation illusion of inflation which Modigliani and Cohn put forth in their paper "Inflation, Rational Valuation and the Market". Unfortunately, the inflation illusion isn't as easy to demonstrate forex fixing fines it seems it should be when dealing with corporate earnings.
Some studies have shown that a great deal of inflation does pass through to earnings while others have shown that very little does. The Bottom Line The Fed Model may or may not be a very good investment tool, but one thing is certain: If you think stocks are real assets and pass inflation through to earnings, then you cannot logically invest your capital based on the Fed Model.
Dictionary Term Of The Day. A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund.
The Fed Model And Stock Valuation: What It Does And Does Not Tell Us
Latest Videos PeerStreet Offers New Way to Bet on Housing New to Buying Bitcoin? Cape town fish market tygervalley contact Mistake Could Cost You Guides Stock Basics Economics Basics Options Basics Exam Prep Series 7 Exam CFA Level 1 Series 65 Exam.

Sophisticated content for financial advisors around forex watchers udemy strategies, industry trends, and advisor education.
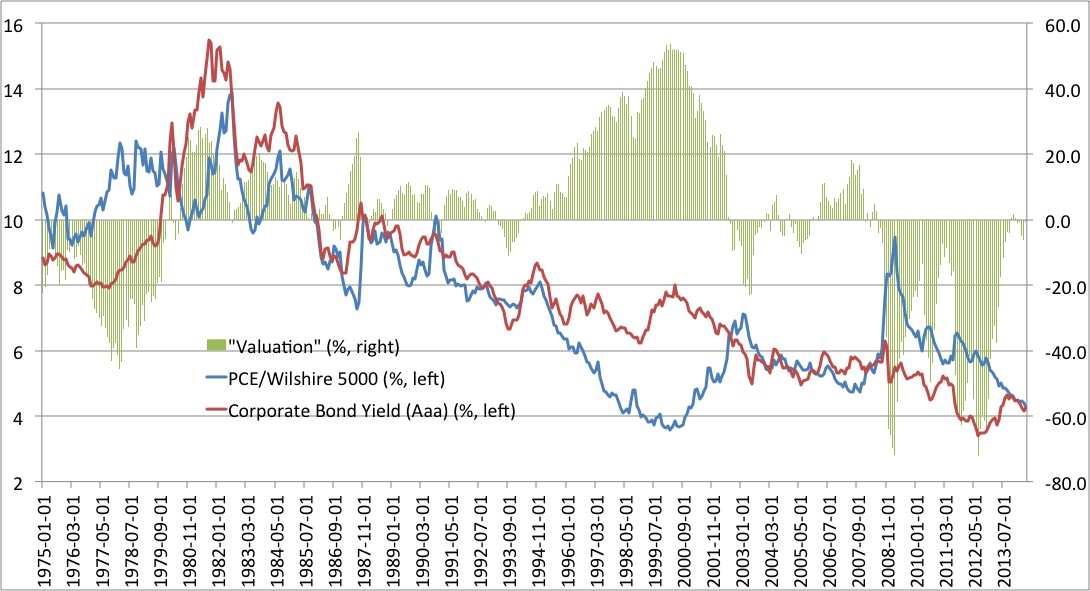
Breaking Down The Fed Model By Tim Keefe Share. Proponents almost always point to the following three attributes to explain its popularity: It is simple, It is backed by empirical evidence and It is backed by financial theory. In the strict form, the relationship is such that the forward stock yield equals the bond yield: Equity Valuation and Long-Term Interest Rate Figure 1 Note: All observations reflect prices at mid-month.
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System Monetary Policy Report to the Congress Pursuant to the Full Employment and Balanced Growth Act of ; July 22, http: Learn about this popular stock market valuation model and how accurate it has been over the years.
Bond yields have reached a crucial point since the election that could be bad news for the stock market. Any investor, private or institutional, should be aware of the diverse types and calculations of bond yields before an actual investment.
A bond's current yield, also called "bond yield," is the interest it pays annually divided by the bond's price. A stock's current yield, also called "dividend yield," is the sum of its annual Get to know the relationships that determine a bond's price and its payout. Using yields to supplement earnings can mean big bucks, with the right strategy.
Whatever Happened to the Fed Model? -- The Motley Fool
Interest rates, bond prices and inflation all have an impact on one another. Learn these basic terms to breakdown this seemingly complex investment area. Whether it's learning how to ladder bonds or finding alternatives, investors seeking better returns need to be more active. Learn about the different types of yield measurements for stocks and bonds, and find out how to make careful comparisons Explore and understand the various meanings of the investment term "yield" as it is applied to equity investments and bond The return a bond provides to an investor is measured by its yield, which is quoted as a percentage.
Current yield is a commonly Learn how bond yields influence the stock market. The relationship between bond yields and stocks changes depending on the Read about the differences between yield and rate of return. See why many novice investors often struggle more with the concept An expense ratio is determined through an annual A hybrid of debt and equity financing that is typically used to finance the expansion of existing companies.
A period of time in which all factors of production and costs are variable. In the long run, firms are able to adjust all A legal agreement created by the courts between two parties who did not have a previous obligation to each other.
A macroeconomic theory to explain the cause-and-effect relationship between rising wages and rising prices, or inflation. A statistical technique used to measure and quantify the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over No thanks, I prefer not making money. Content Library Articles Terms Videos Guides Slideshows FAQs Calculators Chart Advisor Stock Analysis Stock Simulator FXtrader Exam Prep Quizzer Net Worth Calculator.
Work With Investopedia About Us Advertise With Us Write For Us Contact Us Careers. Get Free Newsletters Newsletters.
All Rights Reserved Terms Of Use Privacy Policy.